| What happens when you eat | Diabetes changes what happens when you eat | ||
| During digestion, your body changes most foods into a sugar called Glucose . Glucose enters your blood and travels to your cells. | 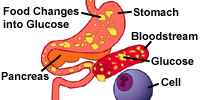 |
 |
With diabetes, your body still changes foods into Glucose. Glucose enters your blood and travels to the cells. |
| During digestion, your body tells the Pancreas to make a chemical called Insulin. Insulin, like glucose enters your blood and travels to your cells. | 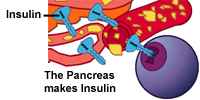 |
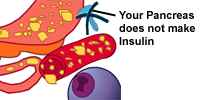 |
Your Pancreas doesn't make insulin, there is nothing to unlock the cells so glucose can enter. It remains in your blood instead making your blood sugar rise. |
| Glucose and insulin meet at your cells. Insulin acts as a key, unlocking the cells to let the glucose enter. Your cells can then burn the glucose to give you energy. | 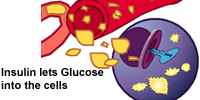 |
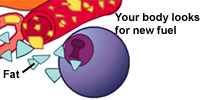 |
Without glucose, your cells try to get energy from stored fat, but fats leave a waste product called Ketones. Ketones build up and cause a dangerous condition called Ketoacidosis. |
Scientists do not know exactly how people get diabetes. but it may be because they do not have a gene that protects against it. They Probably do have some genes that make it possible for them to get diabetes, especially if certain other things happen. For example, a virus, too much stress, or being overweight all seem to add to a person's risk for getting diabetes.
Diabetes is very complicated. Some people's cells do not respond well to insulin. They have to take large amounts of insulin or diabetes medicine to make the insulin/glucose balance work. Other people do respond well to insulin and food, and their blood glucose levels go way up and way down quite quickly.
| Symptoms | |
| Wounds that will not heal Because of nerve damage and poor circulation, diabetics have trouble with sores that heal slowly or not at all. |
Always tired Without insulin, a diabetic's cells are not able to utilize food. This causes weight loss. |
| Always Hungry Since a diabetic's cells are unable to process food, they are virtually starving. |
Blurred Vision The high concentration of glucose in the blood changes the osmotic pressure in the eye , causing the lens to swell. |
| Unexplained Weight Loss Lack of nutrients in the cells causes weight loss. |
Crave Fluids The body eliminates glucose by urination. The loss of fluid causes thirst. |
| Family History Diabetes is more likely to occur if there are family members with the disease. |
Numbness and Tingling of the Extremities Nerve damage is common with diabetes. It is most notable in the feet and hands. |
| Overweight Excess weight is known to bring about diabetes. |
Sexual Dysfunction One of the side effects of diabetes is that men lose the ability to perform sexually. |
| Blood Sugar If diabetes is not treated a person's blood glucose levels can rise to ten times normal. |
Frequent Urination Untreated diabetes will cause frequent urination because the body tries to eliminate excess glucose through urination. |
| If you have any of these symptoms, you should contact your health care provider | |
Having diabetes is not always easy, but people with this condition can live full and happy lives. You do have to think about what and when you eat, how you exercise, and when you take your medication. Everyone, whether they have diabetes or not, should think about what they eat and how they exercise to stay healthy and live long productive lives. A bonus is how good you will feel knowing you are doing well and managing your diabetes.
You are not alone. People can help. Your doctor and nurse, a diabetes educator, a dietitian, your pharmacist, your family and friends can answer your questions, give you helpful tips and support. People who have diabetes sometimes get together and talk about problems and how to work them out. Companies who make insulin and other diabetes care products try to help by making books and offering support groups.
| Diet | Food Chart | Foot Care | Exercise | Gestational | Glossary | Injections | Insulin | Hypoglycemia |